Generative-Ai
2025

PydanticAI Agents Intro
In previous posts, we explored function calling and how it enables models to interact with external tools. However, manually defining schemas and managing the request/response loop can get tedious as an application grows. Agent frameworks can help here.
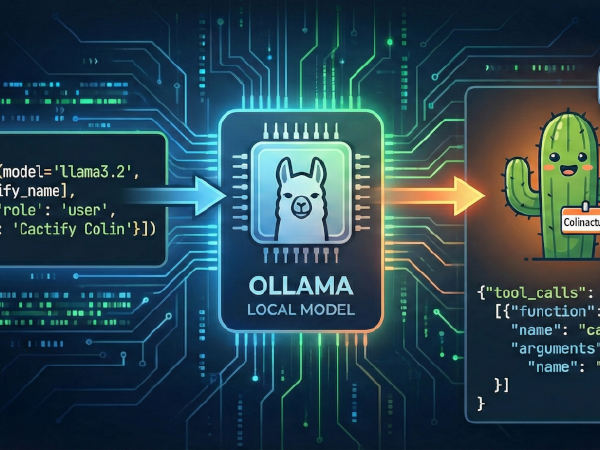
LLM Basics: Ollama Function Calling
In our previous post, we introduced function calling and learned how to do it with OpenAI’s LLMs.
In this post, we’ll call the same cactify_name function from that post using Meta’s
Llama 3.2 model, installed locally using Ollama. The techniques in this post should also work
with other Ollama models that support function-calling.
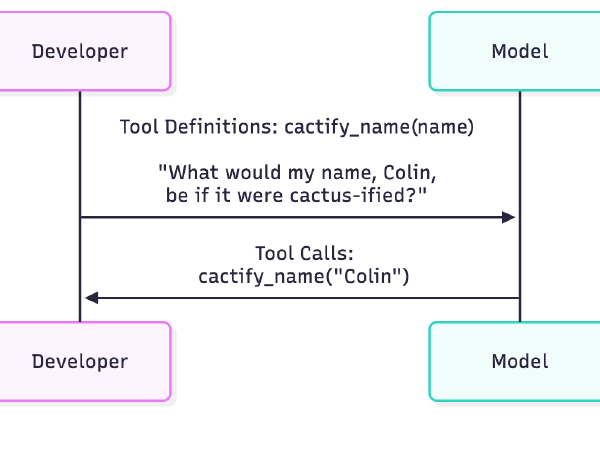
LLM Basics: OpenAI Function Calling
In our previous post, we explored how to send text to an LLM and receive a text response in return. That is useful for chatbots, but often we need to integrate LLMs with other systems. We may want the model to query a database, call an external API, or perform calculations.

Learning LLM Basics with Ollama
We have recently started learning about LLMs and how we can integrate them into our development projects, and we will be documenting our learning in a series of blog posts. In our first installment of the series, we learned about the OpenAI API. In this one, we will experiment with Ollama, which is an open-source application that allows you to download, run, and interact with LLMs on your own hardware. By running models locally, you maintain complete control over your data and can use LLMs without an internet connection. It also allows you to easily experiment with different models.

Learning LLM Basics with OpenAI
For some time now, we’ve been using tools like ChatGPT and CoPilot for day-to-day tasks, but mostly through the conversational AI chatbots they provide. We’ve used them for everything from drafting emails to providing type-ahead coding assistance. We haven’t, however, gone a step further and integrated them into a development project. Honestly, we weren’t sure where to start. Looking into the available options, you quickly run into a dozen new concepts, from vector stores to agents, and different SDKs that all seem to solve similar problems.